Anatomy of the Respiratory System in Children
What is respiration?
Respiration is the act of breathing in and breathing out. When you inhale, you take in oxygen. When you exhale, you give off carbon dioxide.
What makes up the respiratory system?
The respiratory system is made up of the organs involved in the interchanges of gases. It consists of the:
Nose
Mouth
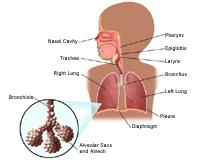
Throat (pharynx)
Voice box (larynx)
Windpipe (trachea)
Airways (bronchi)
Lungs
The upper respiratory tract includes the following:
Nose
Nasal cavity
Sinuses
The lower respiratory tract includes the following:
Voice box (larynx)
Windpipe (trachea)
Lungs
Airways (bronchi and bronchioles)
Air sacs (alveoli)
How do the lungs work?
The lungs take in oxygen. The body's cells need oxygen to live and carry out their normal functions. They also get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product of the cells.
The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made up of spongy, pinkish-gray tissue. They take up most of the space in the chest, or the thorax (the part of the body between the base of the neck and diaphragm). The lungs are covered in a membrane called the pleura. They are separated from each other by the mediastinum. This area contains the following:
Heart and its large vessels
Windpipe (trachea)
Esophagus
Thymus gland
Lymph nodes
The right lung has 3 lobes. The left lung has 2 lobes. When you breathe, the air:
Enters the body through the nose or the mouth.
Travels down the throat through the larynx (voice box) and trachea (windpipe).
Goes into the lungs through tubes called main-stem bronchi:
One main-stem bronchus leads to the right lung and one to the left lung
In the lungs, the main-stem bronchi divide into smaller bronchi
Then the bronchi divide into even smaller tubes called bronchioles
Bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli
Connect with us:
Download our App: